
Broader shoulders and thicker arms for men, round buttocks and toned legs for women – building new muscles improves our body shape and makes us more attractive. But it is also good for your health if you have more muscles – if only because they ensure a higher basal metabolic rate and are therefore an effective means of combating obesity.
Now you’re probably asking yourself: How do my muscles grow? On this page, you will find the answer and useful tips!
Muscle hypertrophy: what happens when you build muscle?
Muscle building – also known as “muscle hypertrophy” – is an adaptive reaction of the body. When a muscle becomes fatigued from very heavy work, such as strength training, it becomes damaged and then repaired. Then it is reinforced a little, i.e. it grows.
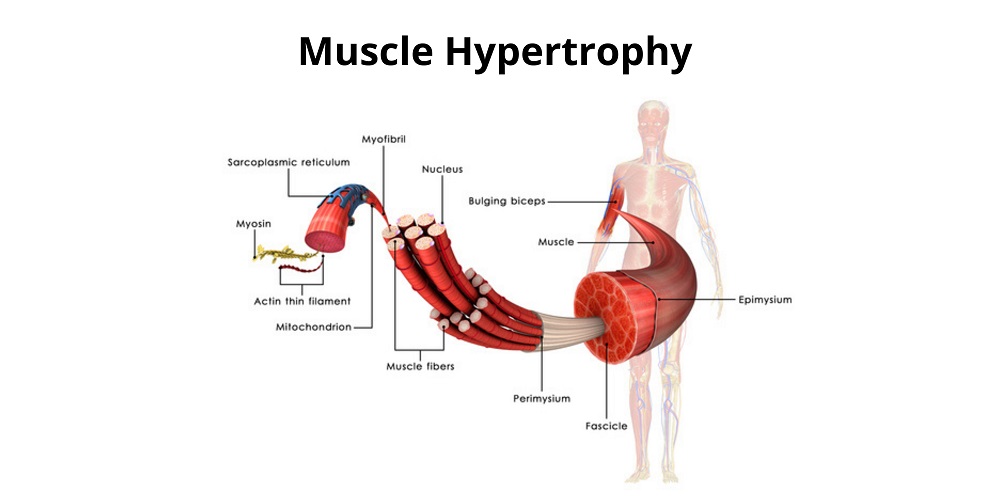
It is important that the stimulus to which the muscle is exposed is “above threshold”. Because only when muscle activity exceeds a certain level (the stimulus threshold) can the muscle no longer do its work without quickly tiring and being damaged. It is only through this damage that the subsequent “supercompensation” gets going, i.e. the repair and strengthening of the tissue. This means: In order to permanently stimulate a muscle to grow, you have to continuously use it to an extent for which it is not equipped (principle of “progressive overload”).
Exactly how muscle hypertrophy works have not yet been fully investigated scientifically. However, it has already emerged that there are three types of hypertrophy:
1) Real build: sarcomeric hypertrophy
Heavy weight training and similar loads exert strong mechanical tensile forces on a muscle, resulting in small damage (microtrauma) to the sarcomeres. Sarcomeres are the individual contractile protein structures within muscle fibers. During post-workout recovery, the body replaces these damaged protein structures and adds some new sarcomeres alongside the old ones, which thickens the muscle fiber.
With continuous training, more and more new sarcomeres are created, which are connected in series and in this way can form new myofibrils – these are the individual contractile, i.e. contractible threads of a muscle fiber. It is therefore also referred to as “myofibrillar hypertrophy”. So this type of hypertrophy only occurs as a result of training with heavyweights, which is why it occurs, for example, in weightlifters. Of course, it goes hand in hand with an increase in strength, since the number of contractile elements, i.e. the sarcomeres, increases.
2) More pump: Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy
With this type of muscle building, no new protein structures are formed; it merely increases the amount of semi-liquid plasma within the muscle fiber. It is primarily glycogen (storage form of glucose, i.e. grape sugar) and the water bound to it that ensures an increase in muscle thickness. This type of muscle growth does not ensure increased maximum strength, but it does increase endurance. However, this hypertrophy is not necessarily permanent, as cells can rid themselves of glucose and water within a few days.
Some of the bodybuilders’ muscle mass is due to sarcoplasmic hypertrophy, which explains why in the vast majority of cases their strength doesn’t match their enormous muscle masses. Although top bodybuilders have more muscle mass than top lifters or powerlifters, they have significantly less maximum strength.
The reason is a different type of training: Bodybuilders only do a few or no maximum strength units and instead concentrate on longer sets with correspondingly less weight: Classically, 8 to 15 repetitions are performed (see below). This type of training largely depletes the glycogen stores in the muscle. During the regeneration phase, these are then refilled and slightly enlarged.
3) The Joker: activation of satellite cells
Humans cannot form new muscle fibers/cells (this process is called “hyperplasia”). However, it is possible to activate and fully develop underdeveloped muscle cells through training. Because these muscle stem cells are located at the edge of the muscle, they are called “satellite cells.” When more muscle cells are active in the muscle, it naturally becomes thicker.
Hypertrophy: The muscle enlarges by storing more nutrients and water. Taking creatine can amplify this process.* New contractile protein structures are also formed, so strength increases over time. However, this only happens if you eat a diet that is high in protein and calories.
Training to failure has been identified as the single most important factor in building muscle. This means you can train with relatively light weights that don’t fully fatigue your muscles for 20-30 reps. According to the latest study results, such training provides the same muscle growth as heavier strength training with 8 to 15 repetitions. However, the strength gain is significantly lower if you choose the lightweights.
Is muscle soreness a prerequisite for muscle growth?
No, muscle soreness is not a prerequisite for muscle growth. It is now assumed that the repair processes of small tears in the muscle and not the acidification caused by lactate are responsible for the sore muscles. But these tears affect the Z-discs between each sarcomere, while the targeted damage in the muscle that eventually leads to muscle growth affects the contractile elements within the sarcomere. So training should damage the muscle, but not necessarily in a way that causes soreness.
Nevertheless, the chance is relatively high that muscle-building training will always cause sore muscles. This is because movements under a heavy load are performed relatively slowly and to failure. Especially if you slowly lower weight during an exercise (eccentric contraction) or, as with butterflies, work far into a stretch, you will probably not only get sore muscles once. But it is also a matter of type whether you tend to have sore muscles.
Muscle soreness does not stand in the way of muscle growth. However, you should not train with (severely) sore muscles. If you regularly have sore muscles, you always have to take longer breaks than would be necessary for terms of super-compensation in terms of muscle building. As a result, the growth stimuli are not set at the optimal frequency, and progress is slowed down. The good side of sore muscles: It is proof that you have actually put a lot of strain on a muscle – which is the goal of the training.
How long does muscle building take?
You’ve probably stumbled across advertisements for workout plans online that make it seem like you can pack on pounds of muscle in a matter of weeks. Such promises are usually underlined with some before and after pictures that are supposed to show just such a blatant transformation. Unfortunately, such plans are completely unrealistic and therefore highly dubious.
In reality, the duration is much longer: Even fast muscle building is done at a leisurely pace. For people who are new to strength training, you shouldn’t expect to see any significant muscle growth for the first four to six weeks as the body first adjusts its nervous system, making better use of the muscle mass that is already there. The strength increases, but the muscles don’t grow with it.
How long does it take to see something?
Only when the body can no longer cope with the demands placed on it by strength training through nervous adjustments alone does it begin to build new muscle mass. However, it still takes a good while until you see something. You have to plan at least three to six months before you are even asked about your new muscles.
Muscles only grow really fast in people who not only do almost everything right in terms of training and nutrition but also start at a very low level. In the ideal case, a very untrained young man can build up about one kilo of muscle per month in the first year of training, which adds up to twelve kilos per year. In the second year of training, it’s only a total of six kilos, in the third three and so on.
In the vast majority of cases, the successes are likely to be somewhat more modest. Anyone who starts strength training as a man between the ages of 25 and 30 and has gained five kilos of muscle after a year has achieved very good results. For women, an increase of two to three kilos after a year is a very good value.
Success factors for muscle building
If you want to be successful in building muscle, you have to work in three areas, the most important points of which we will explain below. Then we also go into the individual differences of trainees.
The three success factors in muscle building:
- Weight training
- Regeneration
- Nutrition

1. Weight Training
The optimal muscle building training plan
The most important factor in muscle building is the training itself. If you don’t train regularly, you don’t build new muscles. That’s why we’ve answered the most important questions about muscle building training here as briefly as possible for you.
2. Regeneration
What is the right level of rest?
Muscles are not built up during strength training, but afterward. In other words, if you train properly, you exhaust your muscles. During the training itself, no new tissue is built up, on the contrary, protein structures are first broken down. Muscle building only gets going after the training: the body rebuilds the damaged structures and then develops some new structures, provided you give it enough time and do not train again too early.
With an optimal training course, which takes the principle of “progressive overload” to heart, you always stimulate a muscle again exactly when the supercompensation, i.e. the muscle growth as a result of the last training session, has reached its peak.
For everyone who is striving to build muscle, this means that the body cannot carry out the supercompensation without sufficient regeneration time between the training sessions, because the tissue is damaged again too soon. The result: muscle building is unnecessarily sluggish, stagnates, or, in the worst case, even turns into systematic muscle loss. Of course, you shouldn’t “recover” for too long, because too long a period of inactivity also eats up muscle mass.
In practice, it is not possible to say exactly when the supercompensation has reached its peak and when the time for the next training has come. That’s why you have to follow the rules of thumb when it comes to regeneration time.
Rules of thumb for the right training time
- Always take at least a full day off before working on the same muscle group again (“48-hour rule”). If you train on consecutive days, use a split plan.
- The harder the training, the longer the break.
- Large muscles regenerate more slowly than small ones.
- If you have to reduce the training weight, although you are fit, have trained regularly, and have not done anything wrong, the breaks are probably too short.
- As long as you have sore muscles, you should not train the corresponding muscles intensively.
- If you have little energy and/or no desire to train for a long time, extend the breaks.
- Adequate sleep is crucial for proper regeneration.
- It should be eight hours to give your body the chance to recover from the ground up at night and be fit for the next (training) day.
3. Nutrition
How do I eat properly?
Properly performed strength training and sufficient regeneration alone are not enough for successful muscle growth; you also need to eat in a purposeful way. After all, this is the only way to get the energy you need for strength training and then give your body the nutrients it needs to build muscle mass. Here is a brief overview of the most important points to consider when building muscle:
- Create a calorie surplus (plus 300 to 500 calories) daily
- Consume a lot of carbohydrates
- Consume lots of protein
- Consume fat in moderation
- Eat a lot of (green) vegetables
- Drink plenty of water
- Trigger insulin release after training
- Prevent catabolic phases with casein and frequent meals
- avoid alcohol
- If necessary, use supplements (protein powder, creatine, mass gainer, etc.)
Supplements – effective helpers in muscle building
The use of dietary supplements is standard in the fitness industry for good reason because natural foods often only cover the special needs of strength athletes to a limited extent. It is also often faster, more convenient, or cheaper to rely on functional muscle-building supplements. Here is a list of the five most useful supplements for muscle building:
- BCAAs
- Protein powder
- Protein bars
- Creatine
- Weight gainer

Individual success factors
A few words about the individual success factors. Because not everyone can make it as far in terms of muscle mass. How fast and how much muscle mass someone can build depends on the following factors:
Nobody can build new muscle mass as quickly as young men between the ages of 15 and 25 because their testosterone release is the greatest. Young women are also better off than older ones, as it takes longer to recover from training as you get older. At what age you should start heavy strength training is very individual and depends on your level of maturity; however, growth should be complete. Many successful strength athletes and bodybuilders started training at a very young age.
On the other hand, even children can do moderate strength training that focuses on correct technique and is mainly carried out with their own body weight, for example in a gymnastics club. There is no upper limit: You can and should do strength training throughout your life to slow down the natural muscle breakdown, keep your bones strong, relieve your joints, and stay mobile overall.
Genes
Everybody is made up in a unique way, which is why some people are better suited to building muscle than others. For example, some people have more muscle fibers than others.[14] Since we cannot form new fibers in the course of muscle building (hyperplasia), but rather thicken the fibers that are present from birth (hypertrophy), the individual amount of muscle fibers limits the potential muscle mass.
In addition, each person has a different distribution of white and red muscle fibers. The general rule is: that the more white, fast-twitching fibers a person have, the more muscle mass they can develop (“sprinter type”). On the other hand, those who have a relatively large number of red fibers are more of the “marathon type” and will find it difficult to build muscle.
Incidentally, this also shows why young age has a positive effect on muscle building: the proportion of red fibers increases with age, i.e. the muscle-building potential decreases. Unfortunately, training can turn white fibers into red, but not red fibers into white.
Gender
As previously mentioned, men produce more of the muscle-building hormone testosterone than women, which means they can build more muscle faster and develop more strength. Muscle building in women is more strongly regulated by other hormones (growth hormones, insulin, and insulin-like growth factors). Women also have fewer and thinner muscle fibers. These genetic differences are primarily reflected in differences in upper body strength and muscle mass.
Starting level/ training age
Der Körper kann nicht unbegrenzt Muskelmasse aufbauen. Je höher das Ausgangsniveau ist, desto weniger Muskelmasse kann noch ausgebildet werden, bis das genetische Limit erreicht ist. Außerdem gilt: Je höher das Trainingsalter ist, desto langsamer geht der Aufbau neuer Muskelmasse vonstatten.
Muscle memory/rebuild
Humans have remarkably good muscle memory. This means that if muscle mass is lost, it can be built up again relatively quickly. Building muscle mass you’ve never had before takes a lot longer.
Anabolic steroids
If anabolic steroids weren’t effective, they wouldn’t be on the doping list as “performance-enhancing substances.” The fact is: There are a variety of chemical aids that significantly accelerate muscle growth and also ensure that the muscle mass that can be achieved far exceeds a natural level.
That’s why a healthy degree of skepticism is always appropriate when moving into the field of weight training and fitness bodybuilding. Under no circumstances should one measure one’s own progress against that of people who, given their very slim but extremely muscular body, may not be “natural”, as they say in the scene.
The necessary mindset
People who fail to build muscle are failing themselves. Despite genetic differences, anyone can build muscle and develop a body that can be described as “muscular” – this also applies to so-called “hard gainers”. But how should you be set up if you want to complete a functioning muscle-building workout?
Purposeful
Building muscle is a long, complex, and sometimes painful process, and it’s not “fun” in the traditional sense. If you are one of those people who like to approach sport in a playful way and do it in groups or clubs, you will probably find it difficult to do systematic strength training regularly and over a longer period of time. Sure, the exercises and training plans are varied from time to time, but there is no such thing as a surprise, drama, the thrill of victory, or a team feeling in muscle-building training.
People who are successful in bodybuilding or fitness training get most of their motivation from themselves and accept that progress is very slow. They also appreciate the strong structure of everyday life that is an inevitable part of strength training and do not see it as a limitation.
Capable of suffering
Even “gentle strength training” that is not carried out to the point of exhaustion of the muscles ensures strength and muscle gains. However, when it comes to effectiveness, it can’t compete with the approach followed by the majority of bodybuilders and fitness athletes: train to failure, i.e. to the momentary fatigue of the muscles.
During the training of this type, the glycogen in the muscle cells is converted into energy without the use of oxygen, a process in which lactic acid (lactate) builds up. The accompanying noticeable burning of the muscles, as well as a trembling during the last repetitions of a set, should be aimed at if you want to optimally stimulate the muscles to grow. Muscle-building training sometimes hurts and you have to struggle through it. You are often rewarded with severe sore muscles – so you continue to suffer for the next few days.
Focused
Anyone who has been doing strength training for any length of time knows that there are different qualities of “muscle feel”. If you get a good muscle feeling during an exercise, you can clearly feel the working muscles, which almost guarantees that the exercise will have an effect and trigger a growth stimulus.
Beginners, on the other hand, often do not know exactly which muscles should be challenged during an exercise or they cannot control the muscles in a targeted manner, which means that they do not work properly. The result: You somehow perform an exercise, but you do not set any effective growth stimuli for the muscles that are to be trained. Too heavy weights are often the reason: To compensate for the lack of strength, swings or other muscles are used, and the results are not there.
In order to achieve a good muscle feeling with every workout, you not only need knowledge of anatomy and good body awareness and coordination, you also have to concentrate on the training. If you want to achieve the best results, you leave the rest of your life outside the gym while you train.
Alternatives to classic strength training
If you now realize that you are not at all the type for years of muscle-building training, as described above on this page, then you still don’t have to write off a muscular body. There are many sports alternatives that may not be as focused on building muscle but are likely to lead to more muscle.
For example, you can start with CrossFit training. This takes place in groups and the training planning is done for you so that you can fully concentrate on the movements. Or you start with a sport like gymnastics, boxing, wrestling, judo, rowing, or climbing where strength training is part of the training or where the sport itself is the strength training.
Seven tips for effective muscle building
- Overload the muscle!
- Pay attention to sufficient regeneration!
- Train regularly!
- Have patience!
- Train with a plan!
- Watch your diet!
- Train your whole life!
You now know how to build muscle and that nothing is given to you. But that’s exactly what makes it so appealing: Can you stick with it and find the right methods for you? If so, you’ll eventually get stuck in the muscular physique you’ve always wanted. You can be damn proud of that because you have achieved something that only a few succeed in doing and that nobody can take away from you anytime soon!
